Pharmaceutical Cold Storage Solutions: Precision Humidity & Temperature Control for Drug Safety
In pharmaceutical cold storage, stringent temperature and humidity standards are critical to ensuring drug stability and patient safety.
Global pharmaceutical cold storage requires compliance with WHO-GDP, USP <659>,
and EU GMP standards, maintaining 2–8°C for refrigerated, -15–-25°C for frozen, and 35–75% RH with ≤±5% deviation.
RSCS delivers precision humidity control and multi-zone monitoring within sealed cold storage environments, safeguarding drug integrity at every stage.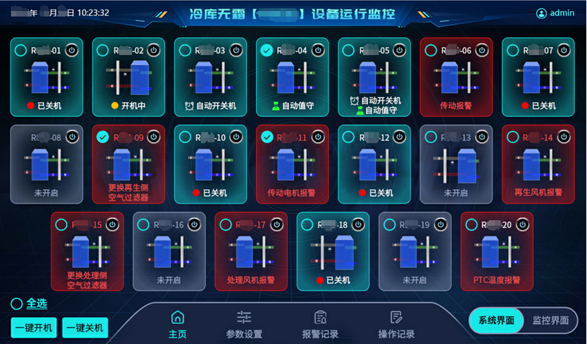
Why Humidity & Temperature Matter
Improper humidity levels directly threaten drug quality:
Excessive Humidity (>75% RH): Causes moisture absorption (e.g., capsule adhesion) and microbial growth (critical for biologics and vaccines).
Insufficient Humidity (<35% RH): Leads to brittleness, packaging cracks, or loss of potency (e.g., dehydration of Chinese herbal medicines).
Biopharmaceuticals and vaccines are particularly sensitive to fluctuations—even minor deviations can accelerate degradation, reducing efficacy or triggering spoilage.
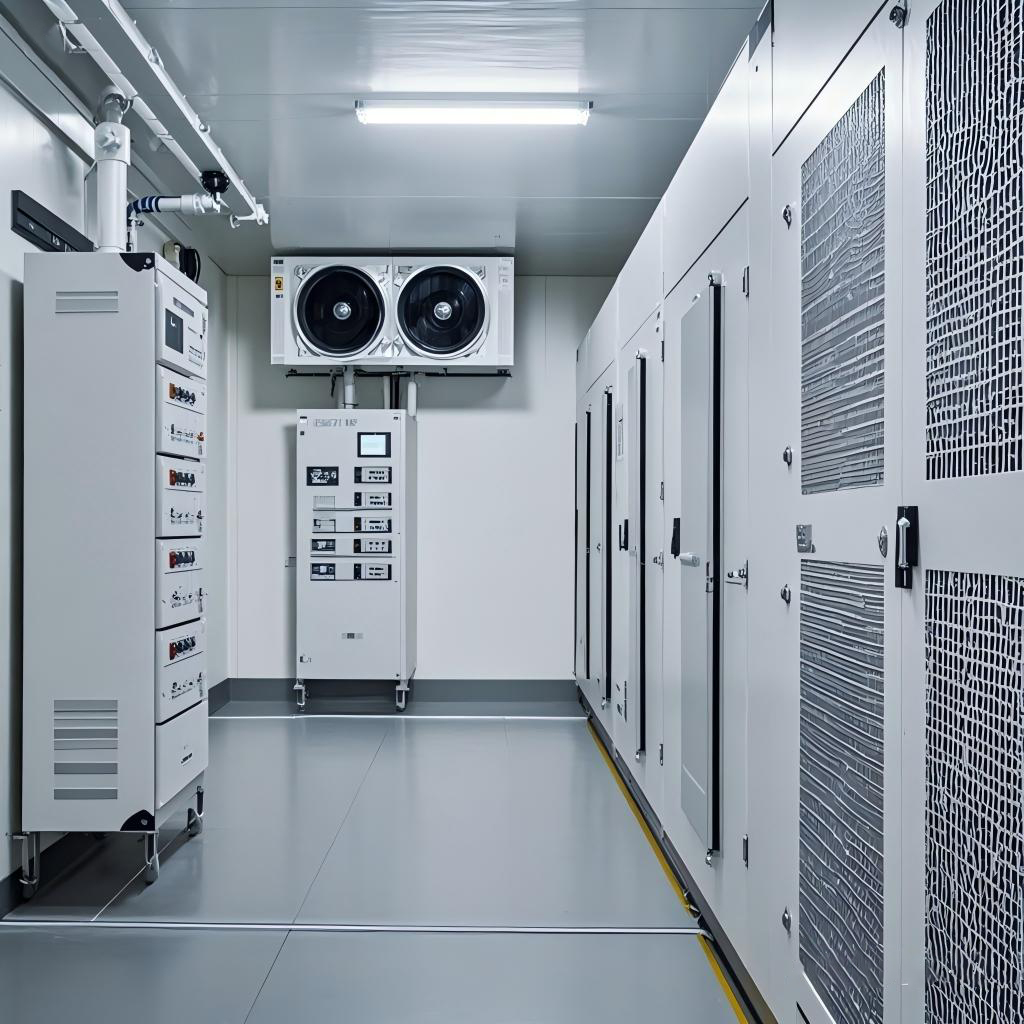
RSCS Technical Advantages
Zoned Precision Control
Intelligent Group Control System: Customizes temperature/humidity settings for distinct storage zones (e.g., vaccines vs. APIs), ensuring compliance with diverse drug requirements.
Sealed Chamber Design: Prevents cross-zone interference and external environmental impacts.
Redundancy & Emergency Response
Backup Systems: Dual cooling circuits and humidity regulators activate automatically during power outages or equipment failures.
Real-Time Remote Monitoring: 24/7 data tracking with alerts for deviations, enabling preemptive corrections before risks escalate.
Regulatory Compliance
Audit-ready data logs for GSP, WHO-GMP, and FDA 21 CFR Part 11 compliance.

Case Study: Stability Assurance
For a Shanghai-based vaccine distributor, RSCS implemented:
Multi-layer humidity buffers to maintain 45%–55% RH for mRNA vaccines.
Redundant cooling loops achieving 99.99% uptime in -25°C ultra-low temp archives.
Integration with ERP systems for automated batch-specific condition tracking.
Result: Zero non-conformance incidents in 18 months, with 30% lower energy costs versus conventional systems.
Why Choose RSCS?
Proven Expertise: 15+ years in GMP/GSP-compliant cold chain solutions.
Patented Technologies: 8+ core patents in humidity stabilization and energy efficiency.
Global Certifications: CE, ISO 13485, and NSF/ANSI 4200 validation.
Safeguard drug efficacy. Optimize operational reliability.
Contact RSCS to design a future-proof pharmaceutical storage system tailored to your needs.


 Return to List
Return to List
 Phone
Phone