Relationship Between Pharmaceutical Cold Storage Operations and Humidity Control
1. Pre-Storage Preparation: Pre-Dehumidification and Packaging Protection
Pre-Dehumidification Treatment
Before storage, products requiring low-temperature preservation (such as vaccines, stem cells, and meat) undergo a drying cycle in a specialized pre-cooling room to remove surface moisture, preventing moisture from being introduced into the cold room and causing frost formation.
Low-Humidity Packaging
High-barrier packaging materials (such as multi-layer aluminum foil or freezer-grade PE bags) combined with desiccants are used to prevent condensation inside the packaging even under –80°C or –196°C environments.
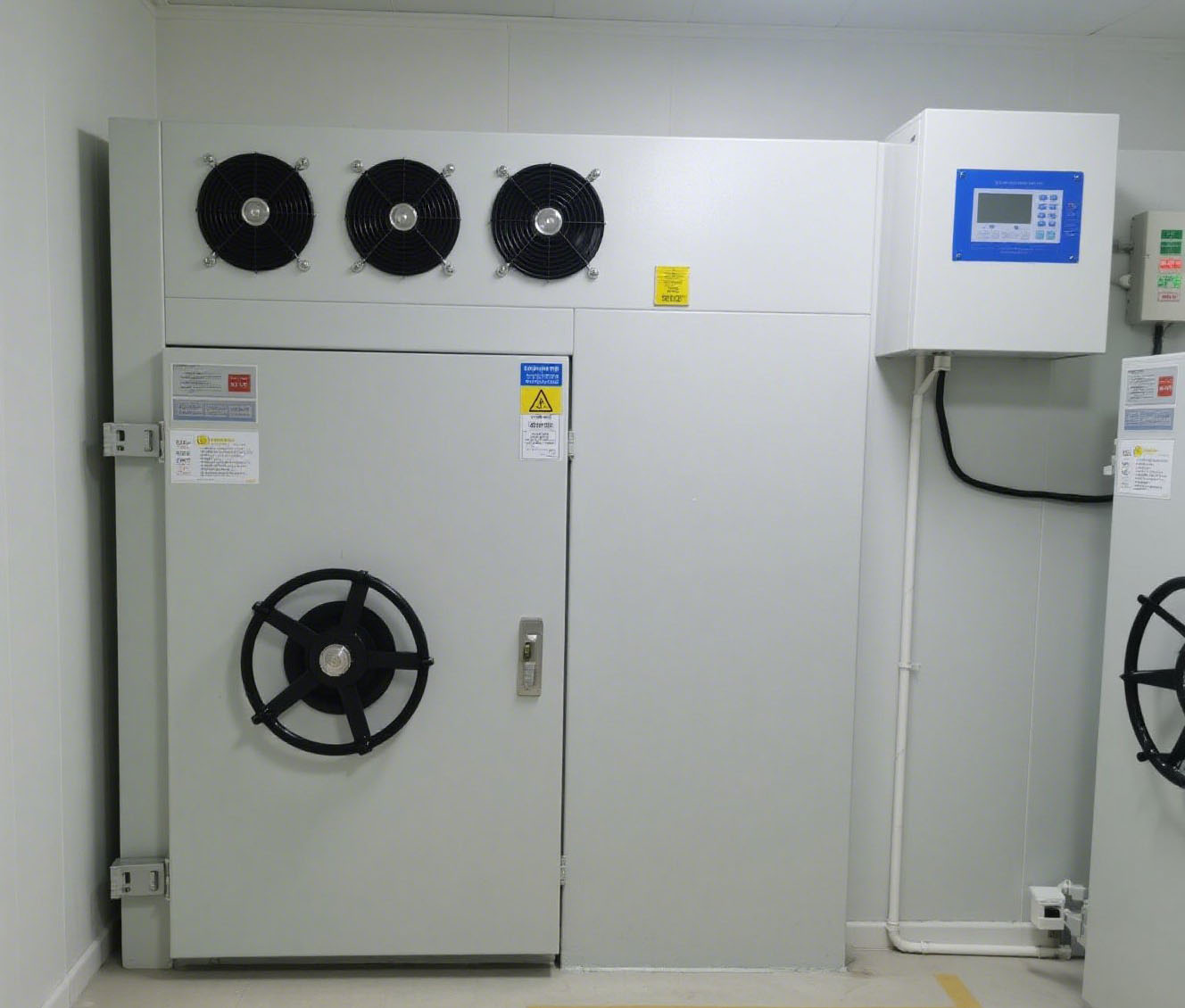

2. Loading and Rapid Operations: Minimizing Humidity Disturbances
Access Control and Air Curtain Systems
Install fast-rolling doors and air curtains to reduce the inflow of humid external air and minimize humidity fluctuations.
Time-Limited Door Operation
Set strict rules to limit door opening time to no more than 3 minutes per instance. Enforce First-In-First-Out (FIFO) and Earliest-Expiry-First-Out (EEFO) principles to reduce humidity and temperature shocks inside the cold storage.
3. Storage and Real-Time Monitoring: Coordinated Temperature and Humidity Management
High-Frequency Sampling
Deploy networked temperature and humidity data loggers with sampling intervals of 1–5 minutes. Alarms are triggered immediately when humidity exceeds preset thresholds (e.g., 30%–60% RH for refrigerated storage, <20% RH for ultra-low temperature storage).
Dry Air Circulation
Utilize dry air circulation systems or condensing dehumidifiers to maintain low moisture levels while preserving temperature, preventing evaporator frost and ensuring frost-free operation.
Uniform Air Duct Design
Design multi-point return and downward airflow layouts to avoid localized high-humidity zones and water condensation, ensuring consistent temperature and humidity throughout the entire cold room.
4. Defrost Maintenance: Intelligent Humidity Regulation
Intermittent Heating Defrosting
In frozen and ultra-low temperature cold storage, intermittent defrosting via gas bypass or electric heating of the evaporator is employed to maintain continuous and efficient humidity control.
Condensate Management
Install automatic drain valves and drip pans to prevent condensate backflow, which could cause humidity fluctuations and microbial growth inside the cold storage.
5. Outbound Operations and Post-Storage Evaluation: Humidity Impact Feedback
Rapid Outbound Operations
Strictly control door opening times during outbound operations. Use mobile air curtains at doorways to further reduce moisture ingress.
Product Quality Testing
Conduct random inspections on key batches after outbound, checking parameters such as moisture content, active ingredient stability, or sensory quality. These evaluations assess the effectiveness of humidity control and provide data for system optimization.
6. Maintenance and Emergency Response: Humidity Recovery Mechanisms
Regular Calibration and Maintenance
Calibrate humidity sensors quarterly and inspect the performance of dehumidification devices. Clean and maintain defrosting and dehumidifying components to prevent dust accumulation from impairing effectiveness.
Emergency Humidity Intervention
In case of system failure or power outage causing excessive humidity, deploy portable dehumidifiers or dry air units immediately, and transfer critical products to backup low-humidity zones to avoid damage.

 Return to List
Return to List
 Phone
Phone